Major risk factors of dementia include:
Many different factors and their interactions can affect a person's chances of developing dementia. For example, not everyone who has high cholesterol develops heart disease and not everyone with heart disease has high cholesterol. However, high cholesterol is still a strong risk factor for heart disease.
A number of subtypes of dementia can be inherited, but most patients will show symptoms before the age of 60 for these cases. Studies have reported that children and brothers or sisters of people with Alzheimer’s disease have a much higher rate of developing this disease, and genes, apolipoprotein E (APOE) and neuronal sortilin-related receptors (SORL1), are also related to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. However, most people with a positive family history or the risk gene will not develop Alzheimer’s disease, so their effect is quite limited.
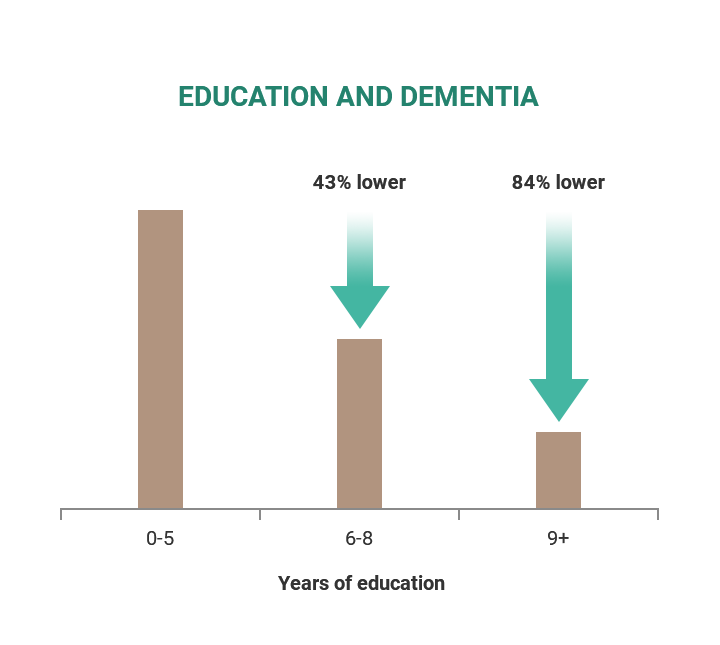
People with higher levels of education have a lower chance of developing dementia. However, education may be related to other factors like family income and health. On the other hand, people who remain cognitively active have a reduced risk of developing dementia despite their education level.
